Let's imagine that when you take a group of beautiful photos and then prepare to use your MacBook to log in to Instagram to upload photos to share your life, you suddenly find that Wi-Fi Not Working on MacBook, I believe this can makes you feel crazy, but don't be worry, we will fix it in no time, so why won’t your MacBook connect to Wi-Fi? Let us see the article below.


Most of us take an always-on wireless internet connection for granted: we're used to it being there when we need it. Unless you're particularly unlucky and plagued by broadband problems, or live in a remote part of the country, fast access to the internet, allowing the streaming of audio and high-definition video, is the norm.
When things go wrong with your Wi-Fi or your broadband connection it's not just your email you'll be missing, but also your social networking life and your evening's Netflix viewing. Equally, if your MacBook has a slow internet connection you can find yourself tearing out your hair.
There are three main reasons why safari no internet connection MacBook: there's a problem with your router, your broadband provider's network is down, or there's an issue with your own Wi-Fi network. Less commonly, there may be an issue with the macOS software you're running. We cover all these scenarios in this article.
Preparation: First, determine what the issue is.
Knowing what's wrong will help you identify appropriate troubleshooting steps of MacBook won't connect to Wi-Fi.
1: Dose the Symptom Occur with More than One WI-FI Device
Wi-Fi issues may be related to the network in question or they may be related to the Wi-Fi computer joining that network. Usually, if other computers or devices (such as Apple TV or iPhone) can get on the Internet without issues, then your Wi-Fi router is probably fine.
If you only have one Wi-Fi device, proceed with this article.
2: Make Sure Your Software is up to Date
Install all software updates available for your MacBook.
If you use a third-party Wi-Fi router, check with the manufacturer to confirm that it has the latest firmware installed. If an update is available, follow the manufacturer's instructions for updating the firmware.
To determine if your Apple Wi-Fi base station firmware is up to date, see Updating your software.
3: Check Your Connections
Some networking issues may be caused by loose or disconnected cables. Verify that all Ethernet and power cables connected between your modem and your Wi-Fi router are correct. Checking that devices such as your router and modem are on,disconnecting and carefully reconnecting Ethernet cables, and replacing damaged Ethernet cables may resolve the issue without any further troubleshooting.
4: Verify that You are Using the Recommended Settings for Your Device
See Recommended settings for Wi-Fi routers and access points.
If your safari, email program, or any of a hundred other Internet-connected apps on your MacBook Pro starts complaining about not having a connection, you may have to do a bit of sleuthing to figure out the cause. After all, a disruption any where along the chain between your MacBook and a distant server could cause an outage,and it's not always obvious where to look.
I suggest trying each of the following steps,in order, until you're able to connect again.
Operations: Secondly, take action to solve the problem of no internet connection MacBook.
1. Try another Site or APP
To make sure the problem isn't restricted to just one website, try visiting another—preferably one that's highly reliable, such as Google.com.
Similarly, to make sure the problem isn't just your current app (such as your email program or Web browser), try connecting to the Internet with another app. If only one site seems to be having problems, try visiting Down for Everyone or Just Me and entering the problematic site's URL. The service will tell you whether computers elsewhere on the Internet can successfully connect to the site.
2. Use Network Diagnostics
Certain types of network problems may cause your browser to display a Network Diagnostics button. This is OS X's way of offering to help debug your connection problem, and I suggest accepting that help. (If you don't see a button, you can launch Network Diagnostics manually. To do this, choose Apple menu > System Preferences and click Network. Click Assist me, and then click Diagnostics.)
The Network Diagnostics utility will guide you through a series of questions and tests, ranging from checking your ethernet or Wi-Fi connection to network configuration and DNS servers. Sometimes the utility can repair problems itself; when it can't, it usually provides more detailed information about the nature of the problem and offers suggestions for solving it.

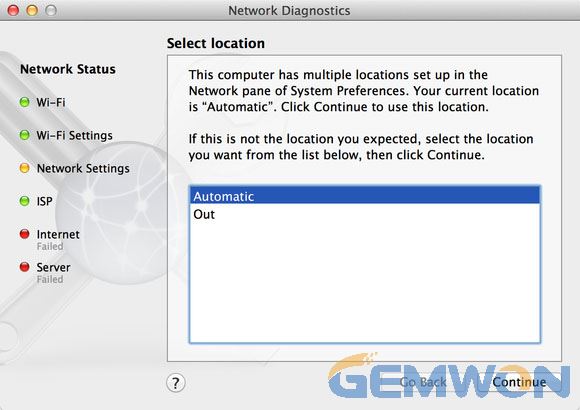
The Network Diagnostics utility built into OS X can track down, and sometimes repair, network connection problems.
3. Nudge WI-FI Back to Life

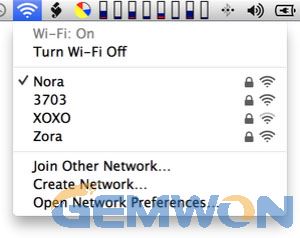
Check your Wi-Fi menu to make sure you haven't gotten onto the wrong network.
If your MacBook connects to the Internet via Wi-Fi, check the Wi-Fi menu (at the top right of your screen) to make sure you're connected to the network you intend to be. MacBooks have been known to hop onto less-desirable networks at inconvenient times.
If the menu's icon has an exclamation point, indicating that it can't successfully connect to any network, try choosing Turn Wi-Fi Off from the menu, waiting about 30 seconds, and then choosing Turn Wi-Fi On.If that still doesn't work, restart your MacBook. Sometimes that's the only way to clear wacky errors that prevent Wi-Fi from connecting.
4. Try Another Device
If you have access to another computer or mobile device that uses the same Internet connection, check to see if you can connect to a website on that device. If not, you can at least rule out your MacBook as the source of the problem and look elsewhere for a solution. But if the other device can connect and your MacBook can’t, even after a restart, skip ahead to the step "Check your DNS settings".
5. Reset Your Router Reset
For network problems that lie beyond your MacBook, if you own or control the network device your MacBook connects to (such as an AirPort base station, Time Capsule, router,switch, or hub), turn that device off, wait about 10 seconds, and turn it back on again. Wait for it to power on completely (sometimes a multi step process that can take several minutes) and try connecting again.
If there’s more than one such device between you and the Internet—for example, an AirPort Express connected to a cable modem-start with the one closest to the Internet and then work your way back to your MacBook, cycling the power on each one as you go.


6. Check Your DNS Settings
The Domain Name System (DNS) enables your MacBook to convert domain names (likeapple.com) into IP addresses (like 17.172.224.47). If the DNS server your MacBook uses is offline, slow, or faulty, you may be unable to connect to any site or service by name. Here's an easy way to check whether DNS is functional if no websites, such as google.com, respond. In Command Prompt ping google.com If it does, then you know your Internet connection itself is fine and the problem is merely looking up domain names.
To fix that problem, open the Network pane of System Preferences and select your network connection in the list on the left. Click Advanced followed by DNS. In the DNS Servers field, you should see one or more IP addresses. If those addresses are enabled (black, as opposed to gray), select each one in turn and click the minus-sign (-) button. Then, regardless of whether there are already addresses there in gray, click the plus-sign (+) button and enter 208.67.222.220; repeat with 208.67.222.222.(These addresses point to Open DNS, a free DNS service that’s often more reliable than the default servers your ISP uses.) Click OK and then click Apply.
Now try connecting again.


If you suspect a DNS problem is preventing you from connecting to the Internet, try entering the IP addresses for the Open DNS servers, as shown here.
Even after following all these steps, success isn't guaranteed, because some outages could be beyond your control. Because of the distributed nature of the Internet, an equipment failure at an ISP can affect more than just that ISP's customers. And on a larger scale, accidental damage to a major fiber optic cable can (and occasionally does) wipe out Internet access to a large region.So, sometimes the only solution to an Internet outage is to wait for it to be fixed. But if the problem lies beyond your local network, your ISP should at least be able to tell you the nature of the problem and an expected repair time.
Conclusion:
Hope you know how to dispose MacBook Pro won't connect to Wi-Fi after reading this post. If this post really helped you, don't forget to share it with your friends. If you still have any further questions, please leave us a message below.
Related Articles:
No Sound on Mac Computer? Try These Solutions
How to Change the MacBook Password
How to Deal with Blinking Laptop Battery Light